As the coronavirus infects human cells



- Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2
- Covered with spikes
- The introduction to the affected cell
- The release of viral RNA
- The infected cells
- Create viral proteins
- Build new copies
- The spread of coronavirus infection
- Immune response against coronavirus
- Leaving the body
- The possible effect of vaccines against coronavirus
- How soap works against coronavirus
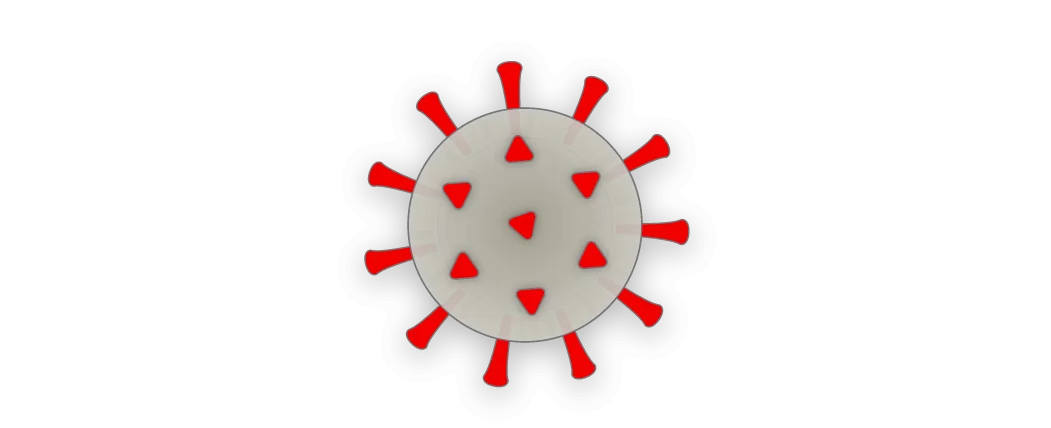
Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2
The virus that causes Covid-19, is currently distributed worldwide. It is known that at least six other types of coronaviruses infect humans, and some cause colds, but the two cause of the outbreak: SARS and MERS.
Covered with spikes
The coronavirus is named after coronarogenic spikes protruding from its surface. The virus is enclosed in a bubble of oily lipid molecules, which disintegrates upon contact with water and soap.
The introduction to the affected cell
The virus enters the body through nose, mouth or eyes, and then attaches to cells of the respiratory tract that produce a protein called ACE2. It is believed that the virus originated from bats, where he could join the same squirrel.
The release of viral RNA
The virus infects a cell, merging its oil membrane with the cell membrane. Once inside, coronavirus releases a snippet of genetic material called RNA.
The infected cells
Virus genome has a length of less than 30 000 genetic “characters”. (We have more than 3 billion.) The infected cell reads the RNA and starts producing proteins, which will keep the immune system in fear and help to collect new copies of the virus.
Antibiotics kill bacteria and not active against viruses. But researchers are testing antiviral drugs, which can destroy viral proteins and to stop the infection.
Create viral proteins
Progression of infection the mechanism of the cell begins to produce new adhesions and other proteins that will form more copies of coronavirus.
Build new copies
New copies of the virus are collected and transferred to the outer edge of the cell.
The spread of coronavirus infection
Each infected cell can produce millions of copies of the virus before the cell is finally destroyed and die. Coronaviruses can infect nearby cells or get into the drops that leave the lungs.
Immune response against coronavirus
The majority of infections Covid-19 cause fever, because the immune system fights to rid himself of the virus. In severe cases the immune system may over-react and begin to attack the cells of the lungs. Lungs clogged with fluid and dying cells, making it difficult to breath. A small percentage of infections can lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome and death.
Recent Posts
How do I create an engaging and informative online quiz or assessment?
Creating an engaging and informative online quiz or assessment can be a powerful tool for… Read More
What are the most effective methods for managing and reducing work-related stress in the hospitality industry?
Work-related stress is a common issue in the hospitality industry, where employees often face long… Read More
How can I improve my assertiveness and communication skills in a leadership position?
In a leadership position, assertiveness and effective communication skills are crucial for success. Being able… Read More
What are the key elements of a successful employee recognition and rewards program?
Employee recognition and rewards programs play a crucial role in motivating and engaging employees, as… Read More
How do I effectively manage and respond to customer feedback and reviews?
Customer feedback and online reviews play a crucial role in shaping a company's reputation and… Read More
What are the best strategies for effective time management as a stay-at-home parent?
Effective time management is crucial for stay-at-home parents who juggle multiple responsibilities on a daily… Read More