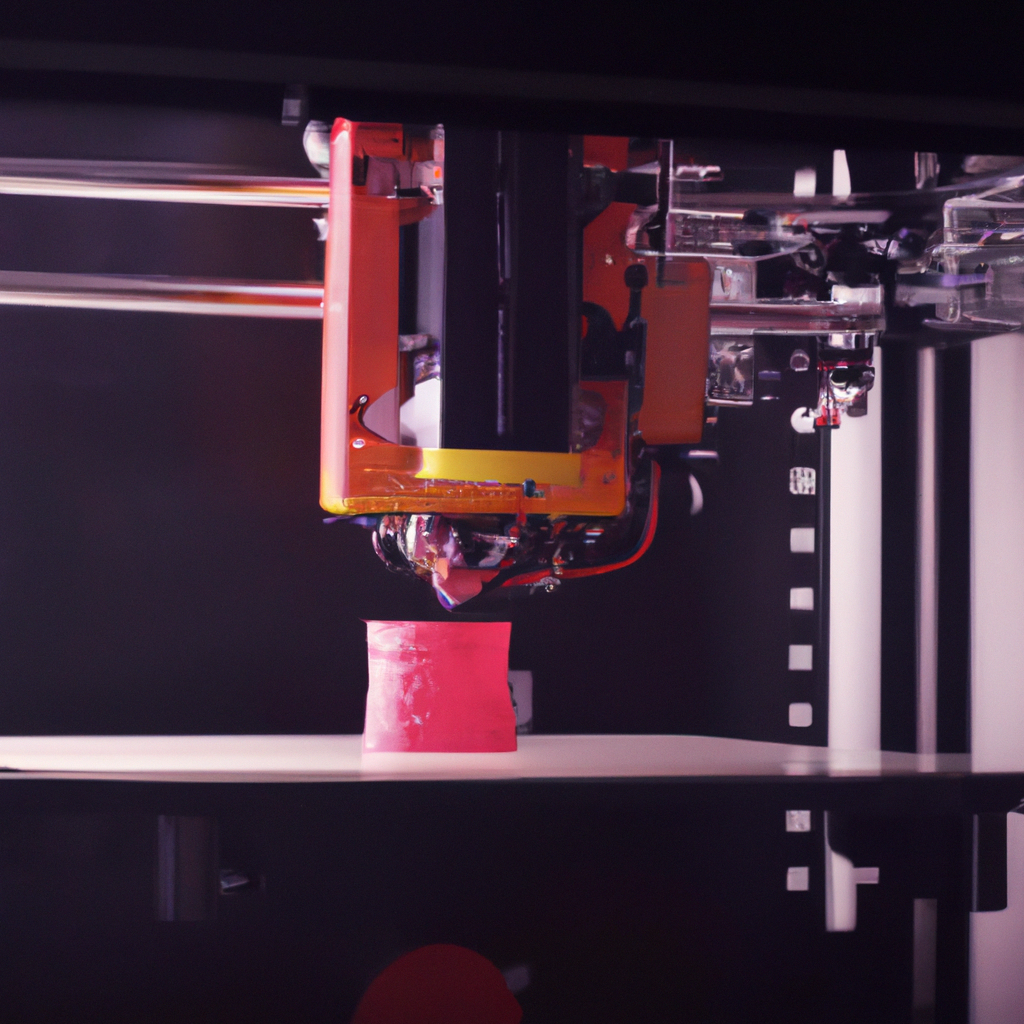
3D printing technology has revolutionized the way we manufacture objects. 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by adding layers of material on top of each other until the desired shape is achieved. It has become a popular manufacturing method due to its efficiency, precision, and versatility. In this article, we will explore how a 3D printer prints objects, the types of 3D printing, 3D printing materials, techniques, applications, and the benefits of 3D printing.
How Does a 3D Printer Print Objects?
The 3D printing process involves three main steps: 3D modeling, slicing, and printing. First, a 3D model is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or 3D scanning. The model can be of any shape or size, and it is saved in a standard file format called STL (Standard Triangle Language).
The next step is slicing, which involves breaking down the 3D model into thin layers, typically ranging from 0.1 to 0.3 mm in thickness, depending on the printer’s capabilities. This is done using specialized software that generates G-code instructions for the printer. The G-code contains information on the position, speed, and temperature of the printer’s nozzle.
Finally, the printing process begins. The 3D printer heats up the material, which is typically a plastic filament or resin, to a melting point and extrudes it through a nozzle. The nozzle moves back and forth, following the G-code instructions, and deposits the material layer by layer until the object is complete.
Types of 3D Printing
There are several types of 3D printing techniques, each with its advantages and limitations. The most common types are:
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is the most popular type of 3D printing, which uses a thermoplastic filament that is heated and extruded through a nozzle. The material solidifies quickly, forming a layer that adheres to the previous layer. FDM is relatively inexpensive and easy to use, but the quality of the prints is not as high as other techniques.
Stereolithography (SLA): This uses a liquid resin that is cured by a UV laser, creating solid layers. SLA produces high-quality prints with intricate details, but it is more expensive and time-consuming than FDM.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): This uses a powdered material, typically nylon or metal, that is heated by a laser, fusing the particles together to create solid layers. SLS is suitable for printing complex geometries and functional parts, but it is also expensive and requires specialized equipment.
3D Printing Materials
3D printing materials come in various types, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even food. The most commonly used material is thermoplastic, which is available in different colors and types, such as ABS, PLA, PETG, and TPU. Metals, such as titanium, aluminum, and steel, are also used in 3D printing, but they require specialized equipment and skills.
Techniques of 3D Printing
There are several techniques used in 3D printing, including:
Support Structures: Some 3D models require support structures to prevent them from collapsing during printing. These structures are printed alongside the object and removed after printing.
Infill: This is the density of the material inside the printed object. Higher infill results in a stronger object but takes longer to print.
Rafting: This is a technique used to improve adhesion between the object and the print bed. A thin layer of material is printed before the object, creating a raft-like structure.
Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing has a wide range of applications, including:
Prototyping: 3D printing is an excellent tool for creating prototypes quickly and inexpensively, allowing designers to test and refine their ideas.
Manufacturing: 3D printing is increasingly used in manufacturing, especially in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
Education: 3D printing is used in education to teach students about design, engineering, and manufacturing.
Art: 3D printing is used in art to create sculptures, jewelry, and other objects.
Benefits of 3D Printing
The benefits of 3D printing include:
Customization: 3D printing allows for the creation of personalized objects, tailored to the specific needs of the user.
Efficiency: 3D printing is a highly efficient manufacturing process that reduces waste and saves time and money.
Innovation: 3D printing has opened up new possibilities for design and manufacturing, allowing for the creation of previously impossible objects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the way we manufacture objects. The process involves 3D modeling, slicing, and printing, using different types of materials and techniques. 3D printing has a wide range of applications, including prototyping, manufacturing, education, and art. The benefits of 3D printing include customization, efficiency, and innovation. With the continued development of 3D printing technology, we can expect to see even more exciting and innovative applications in the future.