A 3D printer is a device that can create three-dimensional objects by adding successive layers of material. It is a technology that has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, and it is now widely used for rapid prototyping, product development, and even in some cases, mass production. In this article, we will explore the 3D printing process, the materials used, the applications, and the future of this technology.
3D Printing Technology
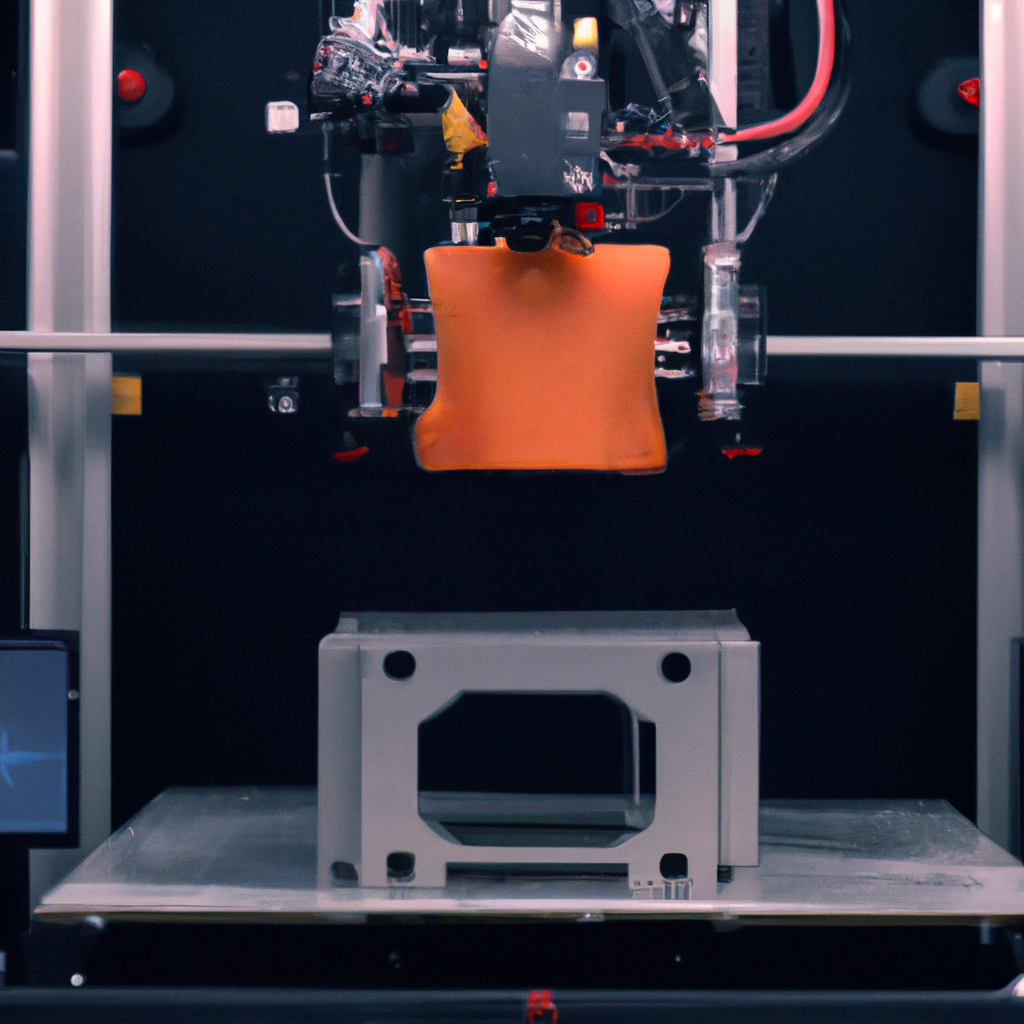
3D printing is a type of additive manufacturing, which means that it builds objects by adding layers of material one on top of the other until the object is complete. The 3D printing process starts with a 3D model, which can be created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or 3D scanning technology. The software slices the model into thin layers, and the 3D printer then builds the object layer by layer.
There are several types of 3D printing technologies, including fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), and digital light processing (DLP). Each technology has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technology depends on the specific application.
3D Printing Materials
There are several types of materials that can be used for 3D printing, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even food. The choice of material depends on the specific application and the desired properties of the object.
Some of the most commonly used materials for 3D printing include:
- Polylactic acid (PLA) – a biodegradable plastic that is easy to print and suitable for creating prototypes and models.
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) – a strong and durable plastic that is commonly used in the production of toys, automotive parts, and household appliances.
- Nylon – a strong and flexible material that is used for creating functional parts such as gears and hinges.
- Metal – metals such as titanium, aluminum, and stainless steel can be used for creating high-strength parts that can withstand high temperatures and pressures.
3D Printing Process
The 3D printing process consists of several steps:
- Design – the object is designed using CAD software or 3D scanning technology.
- Slicing – the software slices the model into thin layers.
- Preparation – the 3D printer is prepared, including loading the appropriate material and calibrating the printer.
- Printing – the 3D printer starts printing the object layer by layer.
- Finishing – the printed object is removed from the printer and any support material is removed.
The printing time depends on the complexity of the object, the size, and the type of material used. Small objects can be printed in a matter of minutes, while larger objects can take several hours or even days.
3D Printing Applications
3D printing has a wide range of applications, including:
- Rapid prototyping – 3D printing allows for the quick and cost-effective creation of prototypes, which can be tested and refined before mass production.
- Product development – 3D printing allows for the creation of customized and complex products, which would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing techniques.
- Education – 3D printing can be used in education to teach students about design, engineering, and manufacturing.
- Medical – 3D printing can be used for creating prosthetics, implants, and even organs for transplant.
3D Printing Industry
The 3D printing industry is growing rapidly, and it is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. The market for 3D printing is expected to reach $35.6 billion by 2024, driven by the increasing demand for customized and complex products.
The future of 3D printing is promising, with new materials and technologies being developed all the time. 3D printing is already being used in space exploration, and it is expected to play a significant role in the development of new technologies such as artificial intelligence and robotics.
In conclusion, 3D printing is a technology that has revolutionized the manufacturing industry. It allows for the creation of customized and complex products, and it is being used in a wide range of applications, from rapid prototyping to medical applications. The future of 3D printing looks promising, and we can expect to see many exciting developments in the coming years.






