A car alternator is one of the most crucial components of a car’s electrical system. It is responsible for charging the battery and powering the car’s electrical components while the engine is running. In this article, we will delve into the working mechanism of a car’s alternator and how it functions in the car’s charging system.
What is a Car Alternator?
A car alternator is a device that generates electricity to power the car’s electrical system and recharge the battery. It is a part of the car’s charging system that works in conjunction with the battery to keep the car running. The alternator is driven by a belt attached to the engine’s crankshaft, which rotates the alternator when the engine is running.
How Does an Alternator Work?
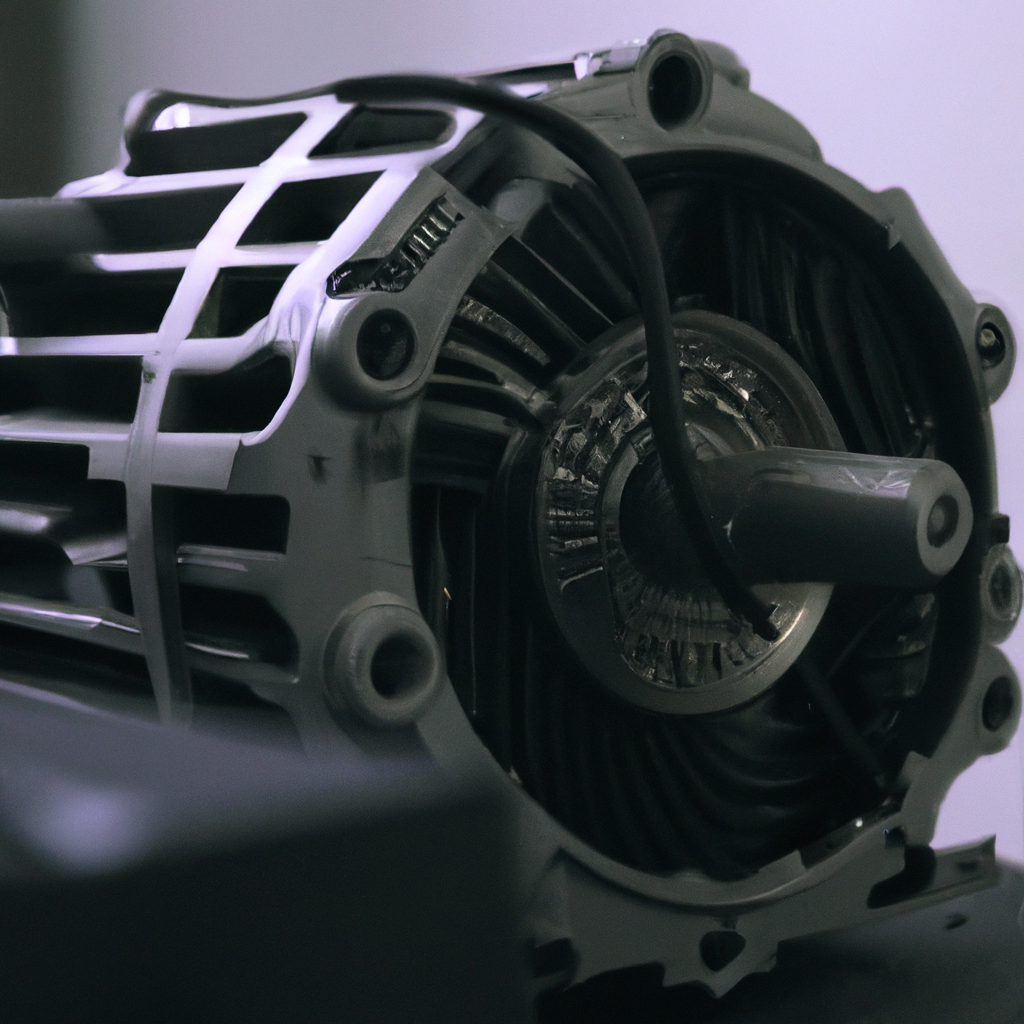
An alternator consists of various components such as a rotor, stator, diode, and voltage regulator. The rotor is a rotating component that creates a magnetic field when electricity passes through it. The stator is a stationary component that contains copper wires that generate electricity when the rotor’s magnetic field passes through them. The diode converts the alternating current (AC) generated by the stator into direct current (DC) that the car’s electrical system uses. The voltage regulator controls the amount of voltage output by the alternator to ensure that the car’s electrical components receive the correct amount of power.
When the engine is running, the crankshaft rotates the belt attached to the alternator, which, in turn, rotates the rotor inside the alternator. The rotation of the rotor creates a magnetic field, which passes through the stator’s copper wires, generating electricity. The diode converts the AC generated by the stator into DC, which the car’s electrical system uses.
The voltage regulator monitors the car’s electrical system’s voltage and adjusts the alternator’s output to ensure that all electrical components receive the correct amount of power. If the voltage is too low, the voltage regulator increases the alternator’s output. If the voltage is too high, the voltage regulator reduces the alternator’s output.
Role of the Alternator in the Car’s Charging System
The alternator plays a critical role in the car’s charging system. When the engine is running, the alternator generates electricity that powers the car’s electrical components and recharges the battery. The battery provides electricity to the car’s electrical components when the engine is not running.
The alternator’s output is directly proportional to the engine’s speed. Therefore, when the engine is running at low speeds, the alternator’s output is low, and the battery provides power to the car’s electrical components. As the engine’s speed increases, the alternator’s output also increases, providing power to the electrical components and recharging the battery.
Signs of a Failing Alternator
A failing alternator can cause various problems in the car, such as dimming headlights, a dead battery, and electrical component failure. The following are some signs of a failing alternator:
- Dimming headlights or interior lights
- Difficulty starting the car
- Electrical component failure
- Battery warning light on the dashboard
- Burning smell coming from the engine
If you notice any of these signs, it is essential to have your car inspected by a qualified mechanic.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a car alternator is a crucial component of the car’s electrical system. It generates electricity to power the car’s electrical components and recharge the battery while the engine is running. The alternator’s working mechanism involves a rotor, stator, diode, and voltage regulator. The alternator’s output is directly proportional to the engine’s speed, and a failing alternator can cause various problems in the car. Regular maintenance of the alternator and the car’s charging system is crucial to ensure the car’s proper functioning.