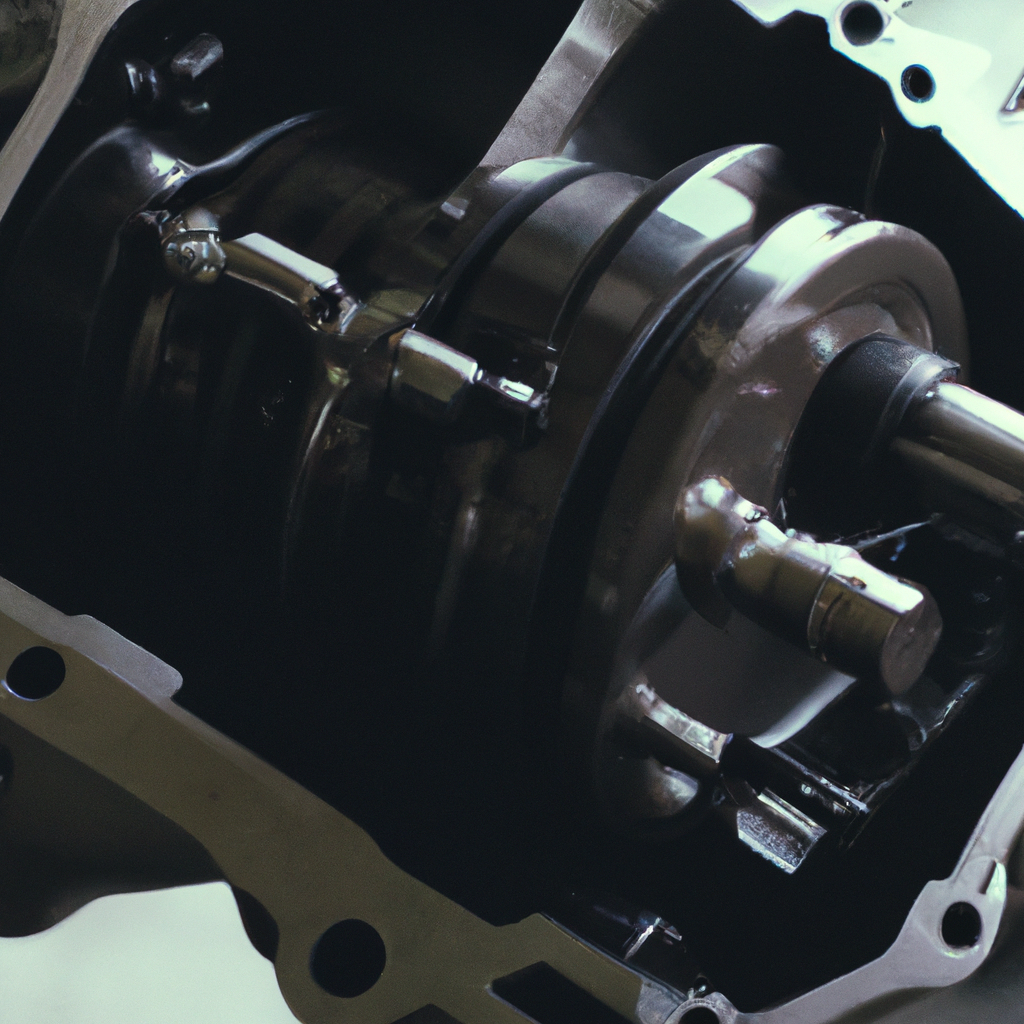
A car differential is an essential component of a vehicle’s drivetrain system, which helps to transfer power from the engine to the wheels. It allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds when turning, providing stability and control while driving. In this article, we will discuss in detail how a car differential works, the differential mechanism, types of differentials, and their functions.
How Does a Differential Work?
The differential mechanism is a complex system of gears that allows the wheels to rotate independently of each other while maintaining a constant speed. The car axle is connected to the differential gear system, which is responsible for transmitting power to the wheels. When a car is moving in a straight line, both wheels rotate at the same speed. However, when turning, the inside wheel rotates slower than the outside wheel.
The differential mechanism works by distributing the power from the engine to the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds. It consists of a set of gears that are housed inside a casing. The pinion gear is connected to the drive shaft and meshes with the ring gear, which is attached to the differential case.
Types of Differential
There are three main types of differentials: open differential, limited slip differential, and positraction differential.
Open Differential
An open differential is the most common type of differential found in vehicles. It allows the wheels to rotate independently of each other, providing smooth handling and good fuel economy. However, it may not be suitable for off-road or high-performance driving.
Limited Slip Differential
A limited slip differential (LSD) is designed to provide better traction and handling in slippery conditions. It limits the difference in speed between the two wheels, ensuring that both wheels receive equal power. LSDs are commonly found in high-performance vehicles and off-road vehicles.
Positraction Differential
A positraction differential, also known as a locking differential, is designed to provide maximum traction and handling in extreme conditions. It locks the two wheels together, ensuring that both receive equal power. Positraction differentials are commonly found in heavy-duty trucks and off-road vehicles.
Function of Differential
The differential serves several critical functions in a car’s drivetrain system. Here are some of the key functions of the differential:
1. Power Distribution: The differential distributes power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring that both receive equal power.
2. Speed Compensation: The differential allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds, compensating for the difference in distance traveled while turning.
3. Handling: The differential provides stability and control while driving, ensuring that the car remains stable and balanced.
4. Traction: The differential ensures that the wheels maintain traction on the road, even in slippery conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the differential is an essential component of a car’s drivetrain system. It allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds, compensating for the difference in distance traveled while turning. There are three main types of differentials: open differential, limited slip differential, and positraction differential. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the driving conditions. Understanding how a differential works and its role in a car’s drivetrain system is essential for safe and efficient driving.