Additive manufacturing or 3D printing technology has been around for many years, and it’s already revolutionized many industries. One of the most promising applications of 3D printing technology is metal fabrication, which offers numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. In this article, we’ll explore how a metal 3D printer works, what the metal printing process entails, and how it’s transforming industrial production, precision engineering, and advanced manufacturing.
How Does a Metal 3D Printer Work?
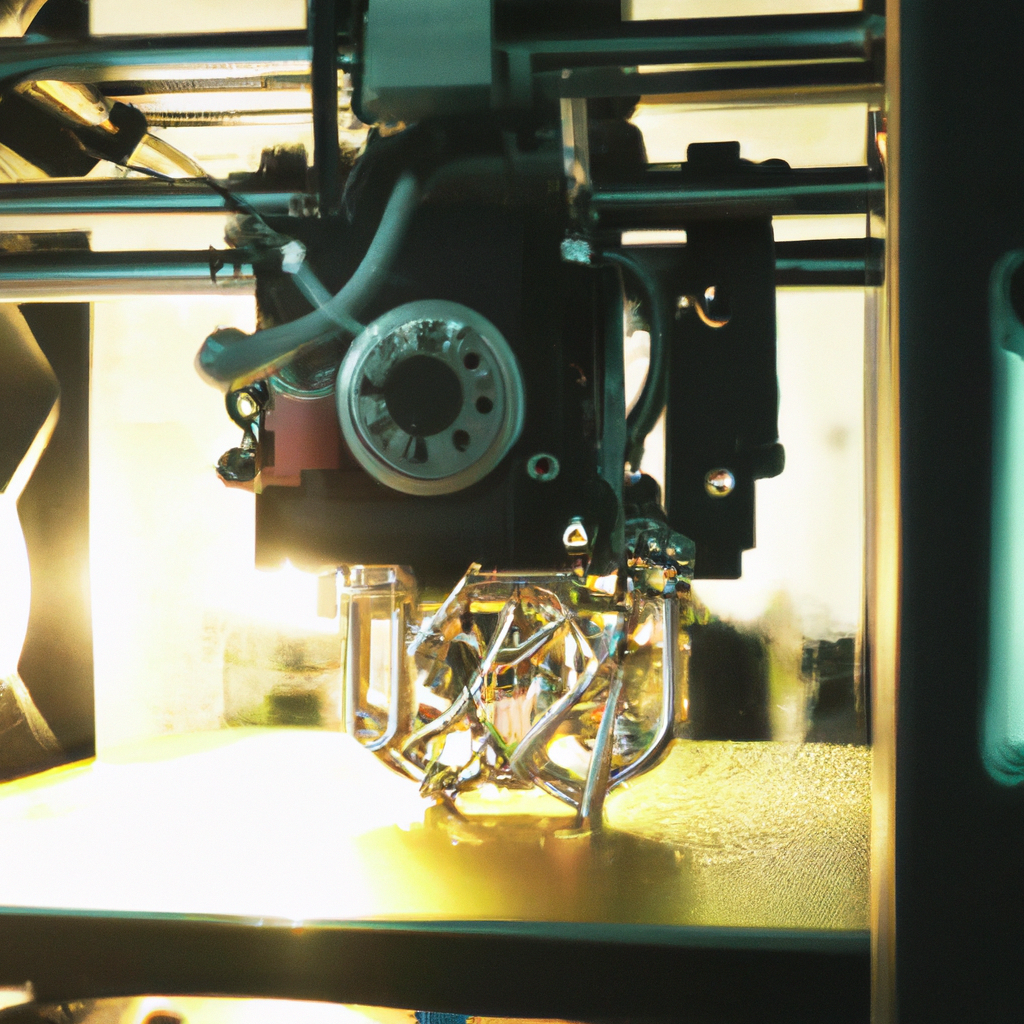
A metal 3D printer is a device that uses additive manufacturing technology to create metal components layer by layer. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which involve subtractive processes such as cutting, drilling, or milling, 3D printing builds up material in a controlled and precise manner. The metal printing process typically involves the following steps:
1. Designing the Part: The first step in metal 3D printing is to create a digital 3D model of the part you want to produce. This can be done using computer-aided design (CAD) software or by scanning an existing object with a 3D scanner. The software then slices the digital model into thin layers, each of which will be printed sequentially.
2. Preparing the Metal Powder: To create a metal part using a 3D printer, you need to start with a fine metal powder. This powder is typically made of titanium, steel, aluminum, or other metals, and it must be carefully prepared to ensure uniformity and consistency. The metal powder is then loaded into the printer’s build chamber.
3. Printing the Part: Once the metal powder is loaded, the printing process can begin. The printer uses a high-powered laser or electron beam to melt and fuse the metal powder together, layer by layer. The laser or beam is precisely controlled by the printer’s software, which follows the digital model to create the desired shape and structure.
4. Post-Processing: Once the printing is complete, the metal part must undergo several post-processing steps to remove excess powder, smooth the surface, and strengthen the structure. This may involve sandblasting, polishing, heat treatment, or other techniques, depending on the metal and the application.
What Are the Advantages of Metal 3D Printing?
Metal 3D printing offers numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing methods, especially in terms of precision, complexity, and customization. Here are some of the key benefits of metal 3D printing:
1. Precise and Repeatable: Metal 3D printing can produce parts with extremely high precision and accuracy, down to a few microns. This level of precision is difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
2. Complex and Intricate: 3D printing allows you to create complex and intricate shapes that would be difficult or impossible to produce with traditional manufacturing methods. This is especially useful for parts with internal channels, undercuts, or other complex features.
3. Customizable and Flexible: Metal 3D printing enables you to customize each part to meet specific requirements, such as size, shape, strength, or weight. This is particularly useful for small-batch or one-off productions, where traditional manufacturing methods would be too expensive or time-consuming.
4. Cost-Effective and Sustainable: Although metal 3D printing can be more expensive than traditional manufacturing methods for large-scale productions, it can be cost-effective for small-batch or one-off productions. Moreover, 3D printing generates less waste and uses less energy than traditional manufacturing methods, making it a more sustainable option.
How Is Metal 3D Printing Transforming Industrial Production?
Metal 3D printing is already transforming many industries, from aerospace and defense to automotive and medical devices. Here are some of the ways metal 3D printing is changing the face of industrial production:
1. Faster and More Efficient: Metal 3D printing can reduce lead times and improve production efficiency, especially for small-batch or one-off productions. This enables companies to respond more quickly to changing market demands and stay ahead of the competition.
2. Lightweight and Strong: Metal 3D printing can produce lightweight and strong parts that can be optimized for specific applications. This is especially useful for aerospace and defense industries, where weight and strength are critical factors.
3. Customizable and Personalized: Metal 3D printing enables companies to customize each part to meet specific requirements, such as size, shape, or performance. This is particularly useful for medical devices, where customized implants or prosthetics can improve patient outcomes.
4. Innovative and Sustainable: Metal 3D printing enables companies to explore new design possibilities and create innovative solutions that were previously impossible. Moreover, 3D printing generates less waste and uses less energy than traditional manufacturing methods, making it a more sustainable option.
Conclusion
In conclusion, metal 3D printing is a game-changing technology that is transforming the world of industrial production, precision engineering, and advanced manufacturing. By enabling precise and repeatable production of complex and intricate parts, metal 3D printing offers numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. As the technology continues to evolve and improve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and benefits in the years ahead.